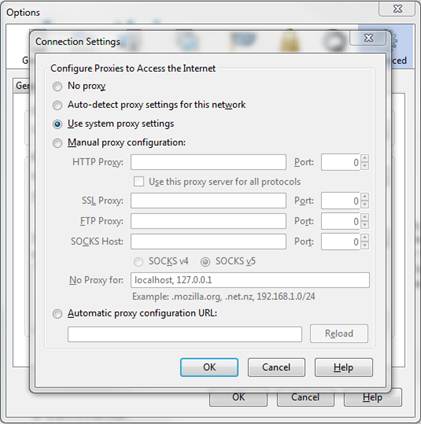
Do you ever get tired of changing your proxy settings inside Firefox to match the settings of the location you are at that day? If you answered yes, then “Use system proxy settings” is for you. When this option is selected, Firefox will set the proxy settings automatically. This has been very useful when moving from our office to a customer site to my house, where each uses different proxy settings. To set your proxy settings to “Use system proxy settings” in Firefox follow the instructions below. [more]
1) Open Firefox
2) Tools > Options > Advanced > Network > Settings > Use system proxy settings