Windows 7 by default installs the Universal Print Driver for HP device and uses the native Windows scanning options. Which is not as robust as the previous versions that came with the All-In-One systems. The user was complaining that the scanning was not usable and needed the same functionality that was there before Windows 7. This method will allow you to install the same software options previously available on Windows XP and Vista. After installation of the software on a Windows 7 PC in Compatibility Mode the following software components are installed:
- Print Driver
- Send Fax
- Uninstall Utility
- User Guide
- Twain and WIA Scan Drivers
-
Copy the entire product CD for Windows Vista 32 bit to the hard drive of the Windows 7 PC.
-
The Windows Vista Full Software Solution on hp.com can also be used. Download the Full Software Solution for your product for Windows Vista from hp.com. Unzip/extract to the hard drive of the Windows 7 PC.
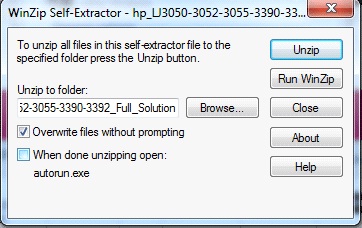
Uncheck the checkbox "When done unzipping open: autorun.exe" before Unzipping the hp.com download bundle. [more]
Figure 1: WinZip Self-Extractor
-
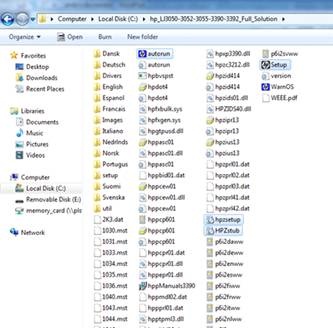
There are 4 executable (.exe) files in the full solution software bundle that are included in the copied/extracted software bundle on the Windows 7 PC hard drive that need to be run in Compatibility Mode for a successful install on a Windows 7 PC.
These 4 files are:
- Autorun (.exe)
- Hpzsetup (.exe)
- Hpzstub (.exe)
- Setup (.exe)
Note: These 4 files may not show the file type extensions (.exe) when listed in the Full Software Solution folder.
Figure 2: Files listed in the Full Software Solution folder
-
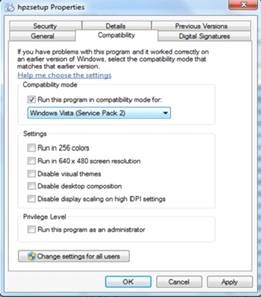
4. Each of these 4 files (autorun, hpzsetup, HPZstub, and Setup) need to be modified to be run in Compatibility Mode on the Windows 7 PC. Right click on each file and go to Properties. Click on the Compatibility tab and checkmark the box Run in compatibly mode for: and select Windows Vista (Service Pack 2) from the dropdown box. Click on Apply or OK . Repeat this step for EACH of the 4 files listed above.
Figure 3: Selecting the compatibility mode
After the 4 files have been set to run in Compatibility Mode, double click the autorun.exe file and allow the installation to begin. Click on Install Software from the top of Begin Setup screen and follow the installation prompts.