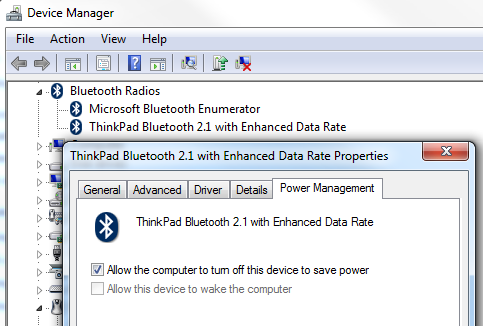
Several of us have noticed that when we shutdown our laptops that the OS seems to stop but the fans do not stop. This is especially harmful when you then put the laptop in a bag and later retrieve it to find it extremely hot. It turns out that there is a problem with Windows 7 when using Bitlocker that exhibits this problem. The details can be found at http://support.microsoft.com/kb/975496. Lenovo has published this patch on the System Update site for the T400.
This is also an issue with Windows Server 2008.