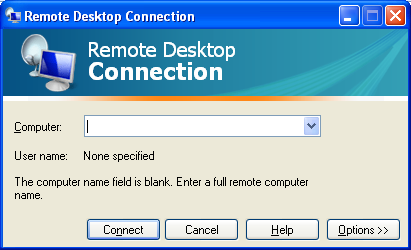
The Remote Desktop Connection client has been updated in XP SP3. Besides the layout changes shown below, one of the changes in RDP 6.1 is the /console switch. To connect to the console of a machine, you must now use /admin bringing the final command to “mstsc /v servername /admin”. [more]